The SFDA has strict labelling and packaging requirements that companies must comply with during the SFDA product registration process. Once approved, the labelling information must not be altered even minimally to maintain product compliance and avoid shipment rejection or withdrawal from the market.
This article will review the labelling requirements for drugs, supplements, medical devices, and food products.
Specific SFDA labelling requirements must be applied to all the drug artwork components, including carton, label, foil, leaflet insert (patient Information Leaflet PIL), and the Summary of Product Characteristics SPC. We will outline here the high-level requirements for each of the abovementioned components as they are one of the leading drug registration requirements in Saudi Arabia.
The product description is to be displayed on more than three non-opposing faces of the box’s six faces. It should be written in English and Arabic.
The active substance’s expression should be presented qualitatively and quantitatively per dosage unit. It should be written in English and Arabic.
The product indication should be highlighted on the pack. e.g. for the treatment of, the prevention of, etc
Excipients with recognised effects or actions should be expressed qualitatively. All excipients must be stated if the medicinal product is parenteral, topical, eye preparation, or used for inhalation.
The contents by weight, volume, number of doses, or the number of administration units should be mentioned (e.g. 10 tablets, 100 mL, etc.).
The method of administration and directions for proper medicinal product use should be clearly stated, e.g. “Shake well before use. For the direction of use, it can be referred to (see enclosed leaflet)
A special warning should be highlighted on the label, e.g., “Protect from sunlight, Keep out of sight and reach of children, for external use only. “
The product storage condition should be mentioned, e.g. Store below 250C or Store below 300C. In-use stability should be added for multidose products, e.g. Shelf life after the first opening is one month, two months, three months, etc. It has to reflect what is stated in the SFDA stability study.
The manufacturer and Marketing Authorization Holder’s Name and Address should be mentioned.
The name and strength of the product should appear over each blister pocket; if the pockets are too small, the information should be repeated in a pattern across the entire strip. It is required in English and Arabic, one of the mandatory SFDA labelling requirements on all parts.
Brand name only is sufficient.
Dates should be expressed as, e.g. 02/2010 or Feb 2010.
The batch (lot) number and expiry date should be at the end of each blister strip.
Although the SPC or SmPC is not printed and enclosed with the drug product, the SFDA labelling requirements must be applied. Only the approved SmPC can be circulated to the practitioners and used for promotional materials.
Name of the medicinal product, strength, and pharmaceutical form.
The active substance should be expressed as a dose per unit. A standard statement should be included for excipients, e.g., ‘For a full list of excipients, see section’ list of excipients. ‘
The product dosage form should be mentioned, e.g., Film-coated tablet, sustain-release tablet, etc., along with a description of the dosage form. If the tablets are designed with a scoreline, information should be given, whether to facilitate breaking or to divide the pills into equal doses.
The indication should define the target disease or condition for treatment or prevention and its indication in adults, neonates, infants, children, and adolescents of age (months, years).
Dose recommendations should be specified per dose interval for each category where appropriate (determine age/weight/body surface area of subsets of the population as proper. Information on special populations like elderly patients, renal impairment, hepatic impairment, and pediatric population should be provided. Also, preventive measures for handling and administering the product should be provided.
The situation of medicinal products must not be given for safety reasons, i.e. hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the excipients.
Information on specific risks, specific risk minimisation measures, adverse reactions, safety information,
Clinical interaction study (in-vivo), Pharmacodynamic interaction, Pharmacokinetic interaction.
Recommendations for use in pregnant and lactating women and women of childbearing potential should be according to clinical trials, non-clinical studies, and pharmacological activity.
Summary of the safety profile, adverse reaction, and national authority address for reporting any side effects.
Effect of different dosing levels taken accidentally, by mistake or by suicide attempts.
The contents should be mentioned by weight, volume, number of doses, or number of units of medicinal product administration (e.g., 10 tablets, 100 mL, etc.).
Special requirements for disposal, if not “no special requirements” can be mentioned. The disposal should be as per the local requirements.
The invented name, strength, pharmaceutical form, active ingredient, therapeutic indication, and benefit of using this medicine.
Contraindication, appropriate precautions for use/special warnings, interactions with other medicines/food/drinks, information for use in pregnant or breastfeeding women, information on fertility, driving and using machines, and excipient’s warnings.
Dosage, Method and route(s) of administration, frequency of administration, Instructions for proper use, Duration of treatment, overdose, irregular use of medicine,
Description of side effects, additional side effects in children and adolescents.
Particular direction and precaution during storing and storage conditions.
Active substance(s) and excipient(s) information, Pharmaceutical form, nature and contents of container, name and address of the marketing authorisation holder and the manufacturer responsible for batch release, the revision date of PIL, and National authority address for reporting any side effect.
The SFDA labelling requirements for medical devices must be applied to the packaging materials, labels, and instructions for use (IFU). They must be submitted accordingly in the SFDA medical device registration applications (MDMA). They are applicable for both low and high-risk medical devices.
The term labelling is a collective term comprising:
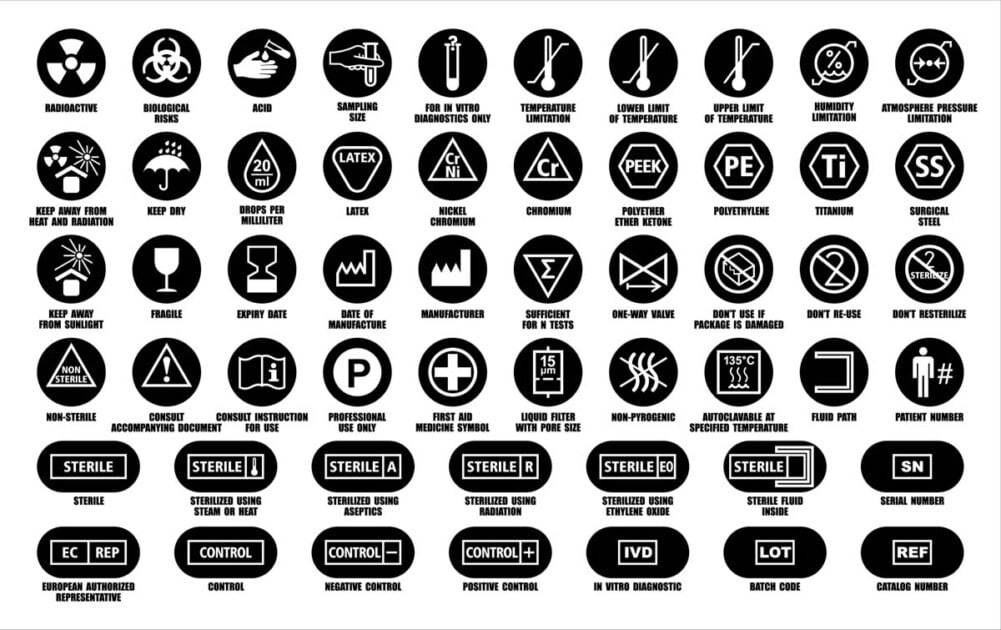
The term label describes written, printed, or graphic information that is:
The primary purpose of labelling is to:
The term “Instructions for Use (IFU)” means the information provided by the manufacturer to inform the device user:
IFU may not be needed or be abbreviated for devices if they can be used safely and as intended by the manufacturer without any such Instructions For Use (e.g., Optical lenses, walking sticks or simple wound dressings).
Where the user of the medical device is:
In both situations, the text shall be written in terms readily understood by the intended user, commensurate with their technical knowledge, experience, education, or training.
Instructions for handling, storage, transportation, installation, maintenance, and disposal of the medical devices shall be in English and, where justified, in Arabic. The text shall be written in terms readily understood by the intended user, commensurate with their technical knowledge, experience, education, or training, where persons without medical qualification may undertake such work. Where the device is designed to be used by laypersons, instructions for handling, storing, transporting, and maintaining the medical devices shall be in Arabic and English.
Labels shall be provided in a human-readable format but may be supplemented by machine-readable forms, such as radio-frequency identification (RFID) or bar codes.
The product trade or brand name should be printed on the label. Likewise, the product Model No is printed on the label.
The manufacturer’s name & address must be printed on labels, and they must match letter by letter with the address details mentioned in the submitted AR agreement & subsequent AR license. Any discrepancy in address details would lead to the return of the submitted application to SFDA & thus would create complications in acquiring medical device marketing authorisation.
OEM is the abbreviation of Original Equipment Manufacturer, while OBL is Own Brand Labelling.
The legal manufacturer in OEM / OBL cases, where the EU jurisdiction has been selected as the basis of the MDMA application, SFDA considers the manufacturer’s name next to the “Manufacturer Symbol” on the labelling as the legal manufacturer. If this is not applicable, the following documents should be submitted to SFDA:
Where the device is connected to an a/c power supply, an indication of the nominal frequency (60 Hertz) and the voltage values with their tolerances for which the devices have been designed
To indicate that the device is for in vitro diagnostic use if the device is an IVD medical device.
Where applicable, an indication of any special storage and handling condition that applies.
Any warnings, precautions, limitations, or contra-indications.
The batch code/ LOT number or the serial number allows post-market compliance actions to be applied if there is a need to trace or recall the device. However, for accessories of IVD medical devices, this may be substituted with a control number, and for software, it shall be replaced with a version number.
An unambiguous indication of the date until when the device may be used safely (e.g., on devices supplied sterile or single-use disposable devices) where this is relevant.
Where relevant, an indication of the net quantity of contents is expressed in terms of weight or volume, numerical count, or any combination of these or other terms that accurately reflect the package contents.
If the device is intended for single use, an indication of that fact.
We support global Pharma and Medical Devices companies in the Saudi market with professional regulatory services. Send us your request to kick off your SFDA project.
Start Here